CSR and Sustainability Timeline
Events, standards, agreements that have directly or indirectly affected the development of corporate sustainability and responsibility
Events, standards, agreements that have directly or indirectly affected the development of corporate sustainability and responsibility
From the ancient times, there has been a tradition of basing profit-making activity (or, business activity) on ethical principles. As a result of industrial revolution, speedy business development and its increased impact, various aspects of business responsibilities (e.g. work conditions, philanthropy) have come into a spotlight in the Western countries since the second half of the 19th century.
Second half of the 20th century should be considered as the kick point of the modern understanding of Corporate Social Responsibility.
During the last years’ period, the concepts of Corporate Responsibility/Responsible Business and Sustainable Development are getting related more tightly.
The International Labour Organisation adopts the first six International Labour Conventions, including conventions on hours of work, maternity protection, minimum age, unemployment and night work for women and the young
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights is adopted by the United Nations General Assembly
An American economist, Howard Bowen has coined the term “Corporate social responsibility”. In his landmark book “Social Responsibilities of the Businessman” he writes, “CSR refers to the obligations of businessmen to pursue those policies… which are desirable in terms of the objectives and values of our society” This has become the backbone by which modern CSR principles are based. Bowen is often referred to as the father of CSR.
The Equal Pay Act is signed into law in the US, prohibiting wage discrimination between men and women.
Milton Friedman published in the New York Times Magazine his famous article The Social Responsibility of Business is to Increase its Profits.
In it, he argued that a company has no social responsibility to the public or society; its only responsibility is to its shareholders.
„Social Responsibilities of Business Corporations“ published by Committee for Economic Development (CED) of the USA which explored the new expectations that society begun placing on the business sector. It introduced the concept of the ‘social contract’ between businesses and society. This contract brought forward the idea that companies function and exist because of public consent and, therefore, there is an obligation to contribute to the needs of society.
The United Nations Conference on the Human Environment was held in Stockholm, Sweden. The role and responsibilities of business in the society were considered among other issues. The United Nations Environment Programme, or UNEP, was created as a result of this conference.
Establishment of the World Commission on Environment and Development
R. Edward Freeman published „Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Approach“,where he defines his Stakeholder Theory. The theory argues that a firm should create value for all stakeholders, not just shareholders.
UN adopts the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer, a global agreement to protect the stratospheric ozone layer by phasing out the production and consumption of ozone-depleting substances (ODS)
Brundtland Commission of the United Nations provided Definition of Sustainable development
Sweden becomes the first nation to enact a carbon tax.
Professor at the University of Georgia Archie B. Carroll published his article The Pyramid of Corporate Social Responsibility: Toward the Moral Management of Organizational Stakeholders. In this paper, Carroll expanded on areas he believed were crucial when implementing CSR in an organization
UN summit on the Environment and Development held in Rio de Janeiro which led to the Rio Declaration on Environment and Development and adoption of Agenda 21. Two legally relevant agreements were opened for signature, the Convention on Biological Diversity and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) - The UNFCC international environmental treaty, adopted at the Rio Earth Summit in 1992, went into effect on 21 March 1994 with the objective to "stabilize greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system"
John Elkington coined the term “triple bottom line“ to clarify sustainability as the integration of social, economic, and environmental value.
LBG, the global standard for measuring corporate community investment, is founded by a group of six London-based companies.
ISO 14001 was formally adopted as a voluntary international standard for corporate environmental management systems.
Adoption of Kyoto protocol - an international agreement linked to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), which commits its parties to binding emission reduction targets
The Dow Jones Sustainability Indices (DJSI) are launched, becoming the first mainstream sustainable investment indices
United Nations Global Compact (UNGC) was launched by Secretary-General Kofi Annan. UNGC is considered to be the world’s largest corporate sustainability initiative, uniting global companies, business associations, labor and civil society organizations committed to promote 10 principles of GC (principles of responsible business)
The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), an international Non-Governmental Organization, launched the first version of the Guidelines, representing the first global framework for comprehensive sustainability reporting.
UN MDGs - At the Millennium Summit, the world leaders ratified the United Nations Millennium Declaration with its eight Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) and set the international agenda for the following 15 years.
European Commission presented a Green Paper - Promoting a European framework for Corporate Social Responsibility
World Summit for Sustainable development in Johannesburg brought together tens of thousands of participants. Several international treaties have been adopted at the conference, including Johannesburg Declaration.
European Commissions launches European Strategy on CSR - Corporate social responsibility: A business contribution to sustainable development
The Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative is launched. Its aim is to promote the open and accountable management of oil, gas and mineral resources.
Equator Principles Launched. The Equator Principles is a risk management framework, adopted by financial institutions, for determining, assessing and managing environmental and social risk in project finance and is primarily intended to provide a minimum standard for due diligence to support responsible risk decision-making.
EU launched the “European Roadmap for Businesses – Towards a Competitive and Sustainable Enterprise” that outlined the European objectives with regards to CSR for the following years
UN Principles for responsible Investment (PRI) launched. The PRI is the world’s leading proponent of responsible investment. It works to understand the investment implications of environmental, social and governance (ESG) factors and to support its international network of investor signatories in incorporating these factors into their investment and ownership decisions
“Creating Shared Value” is introduced as a business concept by Michael E. Porter and Mark R. Kramer, in an article in Harvard Business Review „Strategy and society: the link between competitive advantage and corporate social responsibility“. The concept was further expanded in the January 2011 follow-up piece entitled "Creating Shared Value: Redefining Capitalism and the Role of the Corporation in Society”.
The central premise behind creating shared value is that the competitiveness of a company and the health of the communities around it are mutually dependent. Recognizing and capitalizing on these connections between societal and economic progress has the power to unleash the next wave of global growth.
ISO 26000 – International Standard on Social Responsibility is issued
UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights launched. The Guiding Principles provides a global standard for preventing and addressing the risk of human rights abuse linked to business activity
The European Commission published the renewed European Union (EU) strategy for CSR for the years 2011–2014
UNEP FI's ‘PSI Initiative’(Principles for Sustainable Insurance Initiative) established to serve as the global framework for the insurance industry to better manage environmental, social and governance risks and opportunities in companies' core business strategies and operations.
The EU issues a Directive on non-financial reporting (EU directive 2014/95/EU) requiring large companies of public interest (listed companies, banks, insurance companies, and other companies designated by national authorities as public-interest entities) to disclose non-financial information on environmental, social and governance matters beginning on their 2018 reports and onwards. Directive applied to approximately 6000 companies in the EU.
On April 1, 2014, India became the first country to legally mandate corporate social responsibility. The new rules in Section 135 of India's Companies Act make it mandatory for large companies of a certain turnover and profitability to spend two percent of their average net profit for the past three years on CSR. Companies are able to develop their own social investment strategies and decide where to invest and implement programs, but the government has recommended particular areas of need, including eradicating hunger and poverty, maternal and child health, HIV, TB and malaria, promoting gender equality and environmental sustainability.
The UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) are launched, emphasizing the role of business in achieving the global development agenda.
CSR Europe launched the Enterprise 2020 Manifesto, a set of priorities for corporate social responsibility across all EU countries. It lays out three, broad strategic priorities for the next five years of sustainable economic growth: Make employability and inclusion a priority across boards, management, and value chains; Stimulate companies to engage as committed partners with communities, cities, and regions to develop new sustainable production methods, consumption, and livelihoods.; Put transparency and respect for human rights at the center of business conduct.
The Paris Climate Agreement signed at the UN Climate Change Conference in Paris. The Paris Agreement’s main aim is to keep a global temperature rise this century well below 2 degrees Celsius and to drive efforts to limit the temperature increase even further to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. It also aims to strengthen countries' ability to deal with the impacts of climate change and support them in their efforts.
The UK Modern Slavery Act is passed. It includes a clause requiring all large companies to publish an annual statement on the measures they are taking to address the risk of modern slavery in their supply chains.
GRI Standards for Sustainability Reporting launched. The GRI Standards are the first global standards for sustainability reporting which enable all organizations to report publicly on their economic, environmental and social impacts – and show how they contribute towards sustainable development.
The UK introduces mandatory reporting on the gender pay gap, applying to all companies with more than 250 employees in the UK
EU Regulation (EU) on sustainability-related disclosures in the financial services sector ("ESG Disclosures Regulation") came into force. It will apply 15 months later (from March 2021). Regulation requires investors to consider financially material environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors in their investment decision-making. It also sets out how financial actors should inform beneficiaries about their compliance with the integration of ESG risks and opportunities. This will apply to private and occupational pension funds, insurance funds, portfolio management and investment advisors.
UN Principles for Responsible Banking launched by 130 banks from 49 countries, representing more than a third of the global banking industry, on 22 and 23 September 2019 in New York City, during the annual United Nations General Assembly.
The Principles for Responsible Banking are a framework for ensuring that signatory banks’ strategy and practice align with the vision society has set out for its future in the Sustainable Development Goals and the Paris Climate Agreement
Launch of “Stakeholder Capitalism Metrics”: The World Economic Forum at the fourth annual Sustainable Development Impact Summit in Davos released the report “Measuring Stakeholder Capitalism – towards common metrics and consistent reporting of sustainable value creation”. Developed by the World Economic Forum’s International Business Council (IBC) with Bank of America, Deloitte, EY, KPMG and PwC, it presents a set of universal environmental, social and governance (ESG) metrics and disclosures that can be used by companies to align their mainstream reporting on performance against environmental, social and governance (ESG) indicators and track their contributions towards the SDGs on a consistent basis.

The International Labour Organisation adopts the first six International Labour Conventions, including conventions on hours of work, maternity protection, minimum age, unemployment and night work for women and the young
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights is adopted by the United Nations General Assembly
An American economist, Howard Bowen has coined the term “Corporate social responsibility”. In his landmark book “Social Responsibilities of the Businessman” he writes, “CSR refers to the obligations of businessmen to pursue those policies… which are desirable in terms of the objectives and values of our society” This has become the backbone by which modern CSR principles are based. Bowen is often referred to as the father of CSR.


The Equal Pay Act is signed into law in the US, prohibiting wage discrimination between men and women.
Milton Friedman published in the New York Times Magazine his famous article The Social Responsibility of Business is to Increase its Profits.
In it, he argued that a company has no social responsibility to the public or society; its only responsibility is to its shareholders.
„Social Responsibilities of Business Corporations“ published by Committee for Economic Development (CED) of the USA which explored the new expectations that society begun placing on the business sector. It introduced the concept of the ‘social contract’ between businesses and society. This contract brought forward the idea that companies function and exist because of public consent and, therefore, there is an obligation to contribute to the needs of society.

The United Nations Conference on the Human Environment was held in Stockholm, Sweden. The role and responsibilities of business in the society were considered among other issues. The United Nations Environment Programme, or UNEP, was created as a result of this conference.
Establishment of the World Commission on Environment and Development

R. Edward Freeman published „Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Approach“,where he defines his Stakeholder Theory. The theory argues that a firm should create value for all stakeholders, not just shareholders.
UN adopts the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer, a global agreement to protect the stratospheric ozone layer by phasing out the production and consumption of ozone-depleting substances (ODS)
Brundtland Commission of the United Nations provided Definition of Sustainable development
Sweden becomes the first nation to enact a carbon tax.
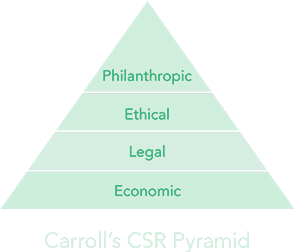
Professor at the University of Georgia Archie B. Carroll published his article The Pyramid of Corporate Social Responsibility: Toward the Moral Management of Organizational Stakeholders. In this paper, Carroll expanded on areas he believed were crucial when implementing CSR in an organization
UN summit on the Environment and Development held in Rio de Janeiro which led to the Rio Declaration on Environment and Development and adoption of Agenda 21. Two legally relevant agreements were opened for signature, the Convention on Biological Diversity and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) - The UNFCC international environmental treaty, adopted at the Rio Earth Summit in 1992, went into effect on 21 March 1994 with the objective to "stabilize greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system"
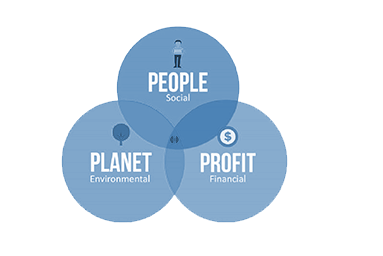
John Elkington coined the term “triple bottom line“ to clarify sustainability as the integration of social, economic, and environmental value.
LBG, the global standard for measuring corporate community investment, is founded by a group of six London-based companies.
ISO 14001 was formally adopted as a voluntary international standard for corporate environmental management systems.
Adoption of Kyoto protocol - an international agreement linked to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), which commits its parties to binding emission reduction targets
The Dow Jones Sustainability Indices (DJSI) are launched, becoming the first mainstream sustainable investment indices
United Nations Global Compact (UNGC) was launched by Secretary-General Kofi Annan. UNGC is considered to be the world’s largest corporate sustainability initiative, uniting global companies, business associations, labor and civil society organizations committed to promote 10 principles of GC (principles of responsible business)

The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), an international Non-Governmental Organization, launched the first version of the Guidelines, representing the first global framework for comprehensive sustainability reporting.
UN MDGs - At the Millennium Summit, the world leaders ratified the United Nations Millennium Declaration with its eight Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) and set the international agenda for the following 15 years.
European Commission presented a Green Paper - Promoting a European framework for Corporate Social Responsibility
World Summit for Sustainable development in Johannesburg brought together tens of thousands of participants. Several international treaties have been adopted at the conference, including Johannesburg Declaration.
European Commissions launches European Strategy on CSR - Corporate social responsibility: A business contribution to sustainable development

The Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative is launched. Its aim is to promote the open and accountable management of oil, gas and mineral resources.
Equator Principles Launched. The Equator Principles is a risk management framework, adopted by financial institutions, for determining, assessing and managing environmental and social risk in project finance and is primarily intended to provide a minimum standard for due diligence to support responsible risk decision-making.

EU launched the “European Roadmap for Businesses – Towards a Competitive and Sustainable Enterprise” that outlined the European objectives with regards to CSR for the following years
UN Principles for responsible Investment (PRI) launched. The PRI is the world’s leading proponent of responsible investment. It works to understand the investment implications of environmental, social and governance (ESG) factors and to support its international network of investor signatories in incorporating these factors into their investment and ownership decisions
“Creating Shared Value” is introduced as a business concept by Michael E. Porter and Mark R. Kramer, in an article in Harvard Business Review „Strategy and society: the link between competitive advantage and corporate social responsibility“. The concept was further expanded in the January 2011 follow-up piece entitled "Creating Shared Value: Redefining Capitalism and the Role of the Corporation in Society”.
The central premise behind creating shared value is that the competitiveness of a company and the health of the communities around it are mutually dependent. Recognizing and capitalizing on these connections between societal and economic progress has the power to unleash the next wave of global growth.

ISO 26000 – International Standard on Social Responsibility is issued
UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights launched. The Guiding Principles provides a global standard for preventing and addressing the risk of human rights abuse linked to business activity
The European Commission published the renewed European Union (EU) strategy for CSR for the years 2011–2014
UNEP FI's ‘PSI Initiative’(Principles for Sustainable Insurance Initiative) established to serve as the global framework for the insurance industry to better manage environmental, social and governance risks and opportunities in companies' core business strategies and operations.
The EU issues a Directive on non-financial reporting (EU directive 2014/95/EU) requiring large companies of public interest (listed companies, banks, insurance companies, and other companies designated by national authorities as public-interest entities) to disclose non-financial information on environmental, social and governance matters beginning on their 2018 reports and onwards. Directive applied to approximately 6000 companies in the EU.
On April 1, 2014, India became the first country to legally mandate corporate social responsibility. The new rules in Section 135 of India's Companies Act make it mandatory for large companies of a certain turnover and profitability to spend two percent of their average net profit for the past three years on CSR. Companies are able to develop their own social investment strategies and decide where to invest and implement programs, but the government has recommended particular areas of need, including eradicating hunger and poverty, maternal and child health, HIV, TB and malaria, promoting gender equality and environmental sustainability.
The UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) are launched, emphasizing the role of business in achieving the global development agenda.
CSR Europe launched the Enterprise 2020 Manifesto, a set of priorities for corporate social responsibility across all EU countries. It lays out three, broad strategic priorities for the next five years of sustainable economic growth: Make employability and inclusion a priority across boards, management, and value chains; Stimulate companies to engage as committed partners with communities, cities, and regions to develop new sustainable production methods, consumption, and livelihoods.; Put transparency and respect for human rights at the center of business conduct.
The Paris Climate Agreement signed at the UN Climate Change Conference in Paris. The Paris Agreement’s main aim is to keep a global temperature rise this century well below 2 degrees Celsius and to drive efforts to limit the temperature increase even further to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. It also aims to strengthen countries' ability to deal with the impacts of climate change and support them in their efforts.

The UK Modern Slavery Act is passed. It includes a clause requiring all large companies to publish an annual statement on the measures they are taking to address the risk of modern slavery in their supply chains.


GRI Standards for Sustainability Reporting launched. The GRI Standards are the first global standards for sustainability reporting which enable all organizations to report publicly on their economic, environmental and social impacts – and show how they contribute towards sustainable development.
The UK introduces mandatory reporting on the gender pay gap, applying to all companies with more than 250 employees in the UK
EU Regulation (EU) on sustainability-related disclosures in the financial services sector ("ESG Disclosures Regulation") came into force. It will apply 15 months later (from March 2021). Regulation requires investors to consider financially material environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors in their investment decision-making. It also sets out how financial actors should inform beneficiaries about their compliance with the integration of ESG risks and opportunities. This will apply to private and occupational pension funds, insurance funds, portfolio management and investment advisors.

UN Principles for Responsible Banking launched by 130 banks from 49 countries, representing more than a third of the global banking industry, on 22 and 23 September 2019 in New York City, during the annual United Nations General Assembly.
The Principles for Responsible Banking are a framework for ensuring that signatory banks’ strategy and practice align with the vision society has set out for its future in the Sustainable Development Goals and the Paris Climate Agreement

Launch of “Stakeholder Capitalism Metrics”: The World Economic Forum at the fourth annual Sustainable Development Impact Summit in Davos released the report “Measuring Stakeholder Capitalism – towards common metrics and consistent reporting of sustainable value creation”. Developed by the World Economic Forum’s International Business Council (IBC) with Bank of America, Deloitte, EY, KPMG and PwC, it presents a set of universal environmental, social and governance (ESG) metrics and disclosures that can be used by companies to align their mainstream reporting on performance against environmental, social and governance (ESG) indicators and track their contributions towards the SDGs on a consistent basis.